Well let me begin by explaining what I feel is the most misunderstood and unexplained item is receiving off-air HDTV – the “digital signal meter” or “signal strength meter” found on most DTV tuners. Some show the strength in terms of a scale of 100, others use signal bars sort of like on mobile phones. In either case, people who watch a channel and tune to this meter feel that if it is lower than desired for a consistent picture, they should add a signal booster or a larger antenna, thinking that the boost in signal will increase that level. So they buy the amp, install it, double check the installation, and notice – NO CHANGE!!!
Allow me to clarify what this level is – contrary to popular belief or implication, it is NOT the amount of off-air signal being received. Rather, it is a measure of the bitrate of the DTV stream for the channel you are viewing. Let me explain the concept of bitrate and how it relates to a good DTV picture. DTV uses the same video compression codec (MPEG-2) as streaming video over the Internet, like some Windows Media or Quicktime videos (though other such streaming videos use the more advanced and supposedly more robust MPEG-4 codec). Perhaps in the Windows Media player you notice a smiling sun or clouds when you are watching a streaming video, and depending on network traffic and the quality of video the picture may freeze up once in a while when the player shows clouds and displays a “Buffering” message. This is because possibly at the time the network traffic is impeding the download speed of your connection, creating errors in the bits (1s and 0s) that the player is unable to decode, so the player wants to stream at a lower bitrate, and reduces the quality of the video.
Your DTV tuner works about the same way, except the bitrate at your tuner is determined by the quality of the signal collected by the antenna. A TV station may send its 1080I HD channel (usually on ##-1) in its DTV bandwidth at a bitrate of 10-12 Mbps in its allocated datastream of about 19.5 Mbps. This allows additional bandwidth in the datastream with program information and a secondary SDTV channel, which I will explain in detail on a later date. Right now I just want to focus on getting a good off-air signal.

To show a visual example, I have attached what a DTV signal looks like on and RF spectrum analyzer (which you can buy if you have $1K-$10K to burn for no good reason), and how it relates to the signal meter. This signal is for KGWB-DT on frequency assignment 41, transmitting at a low power from Burlington, Iowa. The signal is replicated for the Quad City market, served by this station, on a sister digital channel, so this transmission is there to fill a coverage hole and conform to FCC requirements, I suppose. The signal is received indoors in a fairly high-ghosting situation by the Winegard SquareShooter antenna, the nonamplified SS-1000. The first signal you see shows a good-looking DTV signal. Ideally, the signal will have a carrier spike on the far left of the signal and then a plateau. If the plateau is perfectly flat, and the level AT THE RECEIVER is at least 20 dB above the noise floor (what the bottom line on the trace is), then the signal meter should be close to 100%, or 5 bars, or whatever.
 That 20 dB level of the signal above the noise floor is called the “signal-to-noise ratio”, or SNR. The SNR is the TRUE measure of picture quality, and it is set in stone by the antenna. In this case the plateau is not perfectly flat; there is about 5 dB of variation (each vertical grid is 10 dB if case you can see it), but the tuner, which is an early model chipset, is capable of decoding about 85% of the 1s and 0s in the datastream being received, and that is enough to maintain a good quality DTV picture.
That 20 dB level of the signal above the noise floor is called the “signal-to-noise ratio”, or SNR. The SNR is the TRUE measure of picture quality, and it is set in stone by the antenna. In this case the plateau is not perfectly flat; there is about 5 dB of variation (each vertical grid is 10 dB if case you can see it), but the tuner, which is an early model chipset, is capable of decoding about 85% of the 1s and 0s in the datastream being received, and that is enough to maintain a good quality DTV picture.
The next case is in the same location with me rotating the SquareShooter moved just a FEW INCHES from the good spot. In the area there are also nearby FM transmissions and KGWB’s analog 26 channel. There are also reflections due to metal walls in the vicinity of the area where all these signals and harmonics of these signals begin to have a destructive effect on the desired DTV signal.
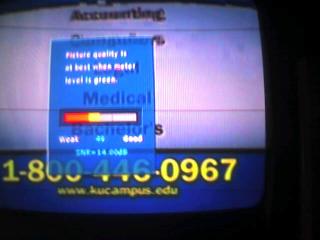 You will notice the carrier spike and maximum level on the plateau has NOT CHANGED MUCH. Yet the interfering signals have created deep valleys in the signal. Now, the same DTV tuner is having serious issues trying to separate the good and the bad, and can only decode about 50% of the KGWB-DT bitstream being transmitted. The DTV picture starts to pixelate, freeze, even disappear. This happens by moving the antenna ONLY A FEW INCHES from a good spot.
You will notice the carrier spike and maximum level on the plateau has NOT CHANGED MUCH. Yet the interfering signals have created deep valleys in the signal. Now, the same DTV tuner is having serious issues trying to separate the good and the bad, and can only decode about 50% of the KGWB-DT bitstream being transmitted. The DTV picture starts to pixelate, freeze, even disappear. This happens by moving the antenna ONLY A FEW INCHES from a good spot.If this were an analog picture, well first of all there would just be a series of “spikes” in the bandwidth, but the viewer would be seeing undesirable patterns and noise in the analog picture. Or, there could be “ghosting” in the picture. At least here at Winegard we had a diagnosis for just about every poor analog picture. You had heavy snow, you need more antenna. Light snow or a grainy picture? A preamp will fix that. If you saw a “herringbone” pattern in the picture, a strong FM signal was present and needed to be filtered. Ghosting, either check you cable or slightly reposition your antenna to make an undesired reflected signal “miss” the antenna. Unfortunately, ANY ONE of these same problems can give your DTV tuner issues in decoding the DTV bitstream, and give you a low reading on the “digital signal meter”. So it is not always a lack of signal at the tuner that is why your DTV picture may be breaking up.
Now I wish to add how amplifiers relate to this issue. The important thing to remember is that an amplifier only increases the signal levels of WHATEVER INFORMATION IS COLLECTED BY THE ANTENNA. The signal may go up, but so will the noise floor, so the TRUE measure of picture quality, the signal-to-noise ratio, does NOT change. In fact, additional noise is created by the amplifier circuitry; the amount of this noise created is related by the Noise Figure (NF) of the amplifier; this is why low-noise amps (LNAs) are highly recommended for DTV reception. Amplifiers will NOT pull in signal collected by the antenna or extend the antenna range. The intention of amplifiers is to offset signal losses in cables, splitters, and diplexers, details I will explain on another date.
So, if an amplifier were used with the antenna in a position where the DTV signal had those deep valleys in the signal, those valleys will still be there at the amplifier output, and the DTV tuner will STILL have issues decoding the signal. As a result, the digital signal meter level will likely NOT change. There are other cases where people have tried using an amp only to find the signal meter got worse! In this case, they may be in a location very close to the TV transmitters (about 25 miles or less). The amplifier is then OVERDRIVING the signal into the DTV tuner, and next thing the viewer knows, the meter goes from nearly 100% to ZERO! In this case the user may have too much antenna with little signal loss in the downlead to a signal tuner. This can be fixed by getting a 6 dB inline VHF/UHF attenuator pad (you can get one at Radio Shack for a couple dollars), and attach it on the antenna input of your DTV tuner, and the antenna cable then connects to the other end of the pad. One other possibility is that the amp is saturating, and introducing undesired harmonics into the good DTV signals, making the digital signal worse. High-gain amplifiers require low signal input levels in order to work properly, so a huge 30 dB amp should only be used in fringe or rural areas WITHOUT NEARBY STRONG TRANSMISSIONS to POSSIBLY make a difference. However, if the SNR at the antenna is less than 20 dB, the amplifier will likely NOT help you, no matter how strong the amp is. You will need a stronger and larger antenna to get more SNR.
So if you are not getting good signal levels after putting up an antenna, before spending money on an amp, try adjusting the antenna a few degrees off its position, or raise or lower the antenna about a foot on the mast. You might find the signal meter shoot up because you tuned out an interfering signal! If you get an antenna, try a direct home run, and use the signal meter to adjust the antenna (80% or better will ensure a consistent DTV picture). If after this you have a couple low signals, then add in the amplifier. And if things suddenly change the next day, it’s because the signal strengths and reflections changed with the weather, and you may need another adjustment until signals hold day after day.
Next week I will have a new post explaining why some types of antennas (bowtie vs Yagi) work better than others in DTV reception, using the concept of the good signal. I will now open this post to comments; if you have a Blogger account, just simply click on the “comments” link below and have your say or question. If you do not have a Blogger account, you can create one for free at http://www.blogger.com/, and use the same username to post your views on other boards powered by Blogger. Take care!
